The Concept of Saturated Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Concept of Saturated Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Concept of Saturated Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Concept of Saturated Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide

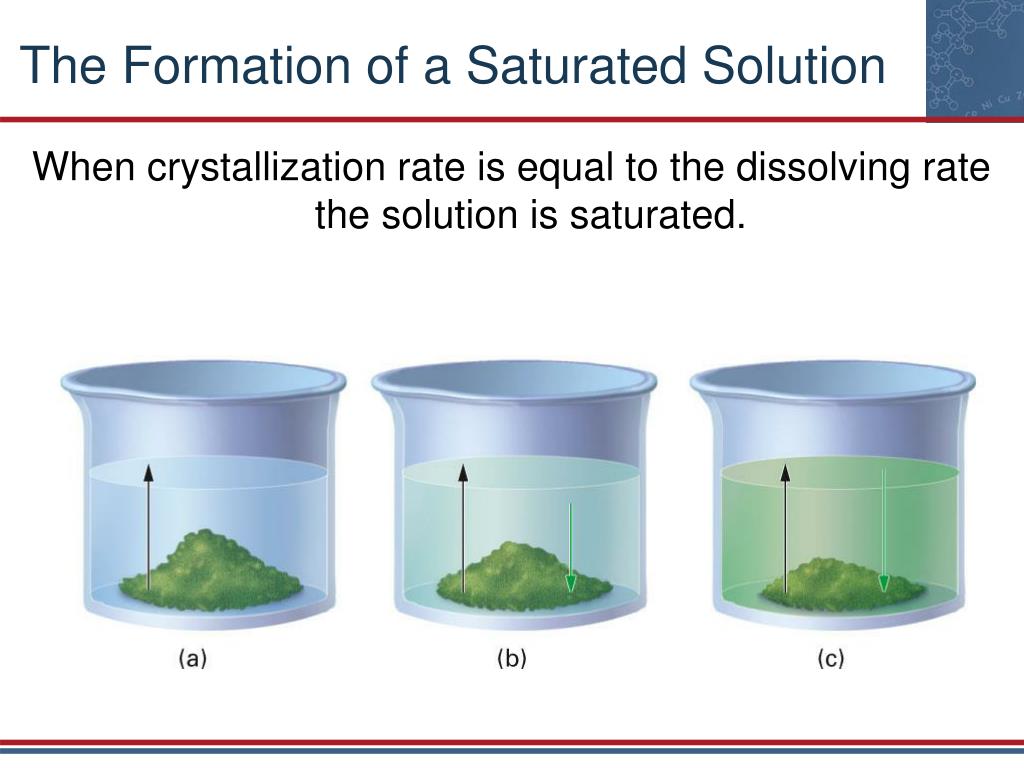
The term "saturated solution" refers to a solution where the maximum amount of a solute has dissolved in a given solvent at a specific temperature. This point of maximum dissolution is reached when the solution is in equilibrium with undissolved solute, meaning the rate of dissolution equals the rate of crystallization.
It’s important to understand that solubility, the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent, is a property specific to each solute-solvent pair and is influenced by factors such as temperature and pressure. For instance, sugar dissolves more readily in hot water than in cold water.
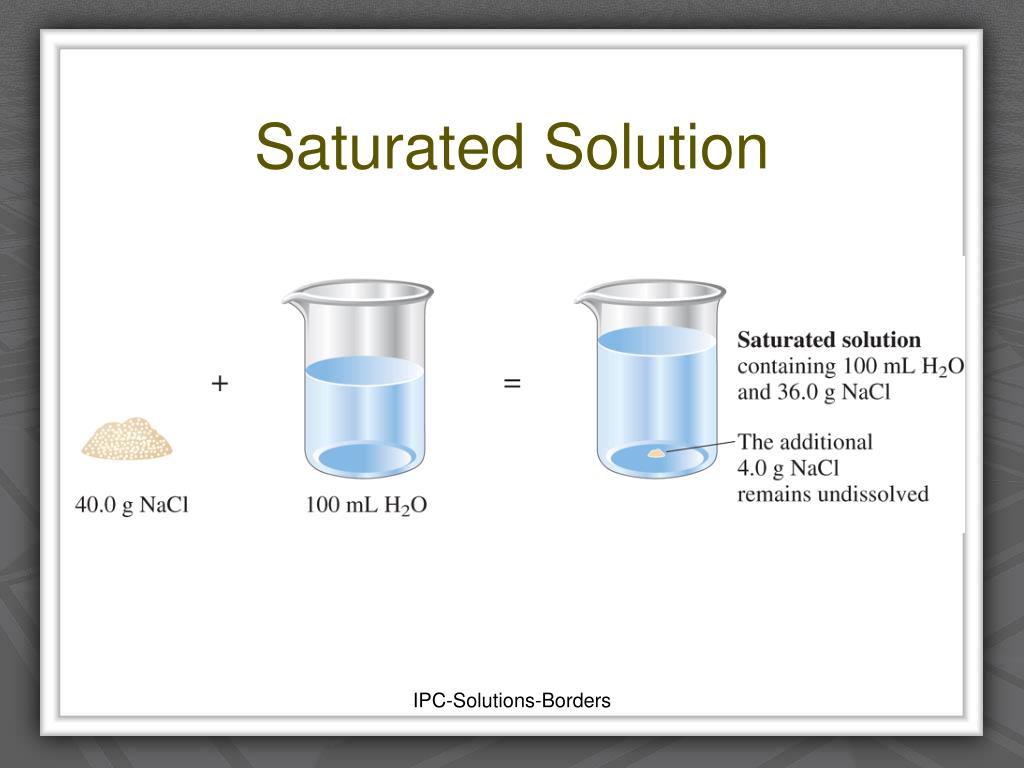
While the concept of saturated solutions is fundamental in chemistry, it is not possible to create a saturated solution with 36 grams of sodium in any solvent. This is because sodium is a highly reactive metal that reacts violently with water, producing hydrogen gas and a highly exothermic reaction. This reaction makes it impossible to dissolve sodium in water or other common solvents to create a saturated solution.
Understanding the Risks of Sodium and Water Reactions
The reaction between sodium and water is a highly dangerous process that should never be attempted without proper safety precautions and expertise. The reaction generates significant heat, potentially causing explosions or fires. The hydrogen gas produced is flammable and can ignite, leading to further hazards.
Alternative Examples of Saturated Solutions
Instead of focusing on the impossible scenario of dissolving sodium, let’s explore examples of how to create saturated solutions with other common substances:
1. Creating a Saturated Sugar Solution:
-
Materials:
- Sugar (sucrose)
- Water
- Beaker or container
- Stirring rod
- Thermometer
-
Procedure:
- Heat a specific amount of water in a beaker to a desired temperature.
- Gradually add sugar to the water while stirring continuously.
- Continue adding sugar until no more dissolves and undissolved sugar remains at the bottom of the beaker.
- Monitor the temperature throughout the process, as solubility changes with temperature.
- Once the solution reaches equilibrium, it is considered saturated.
2. Creating a Saturated Salt Solution:
-
Materials:
- Salt (sodium chloride)
- Water
- Beaker or container
- Stirring rod
- Thermometer
-
Procedure:
- Add a specific amount of salt to a beaker containing water.
- Stir the mixture continuously until the salt dissolves.
- Continue adding salt until no more dissolves and undissolved salt remains at the bottom of the beaker.
- Monitor the temperature throughout the process, as solubility changes with temperature.
- Once the solution reaches equilibrium, it is considered saturated.
Importance of Saturated Solutions in Chemistry and Everyday Life
Saturated solutions play a crucial role in various scientific and industrial applications. Some examples include:
- Crystallization: Saturated solutions are essential for growing crystals. By carefully controlling the temperature and allowing the solution to cool slowly, crystals can be formed from the dissolved solute.
- Recrystallization: This technique utilizes saturated solutions to purify substances. By dissolving a substance in a hot solvent and then cooling the solution, impurities remain dissolved while the desired substance crystallizes out.
- Pharmaceuticals: Saturated solutions are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing to create drug formulations and ensure accurate dosage.
- Food Industry: Saturated sugar solutions are used in the production of jams, jellies, and other food products.
FAQs about Saturated Solutions
Q: Can I create a supersaturated solution?
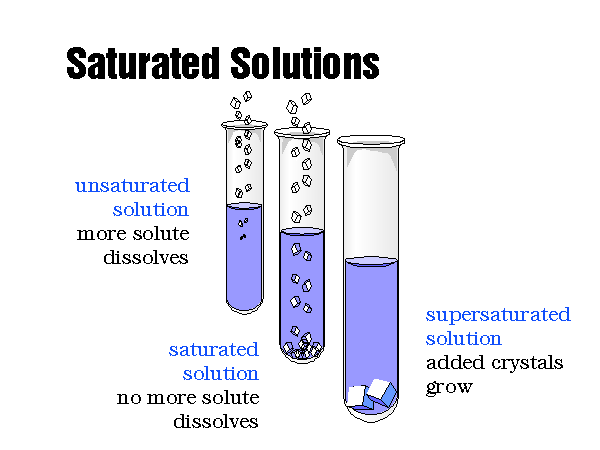
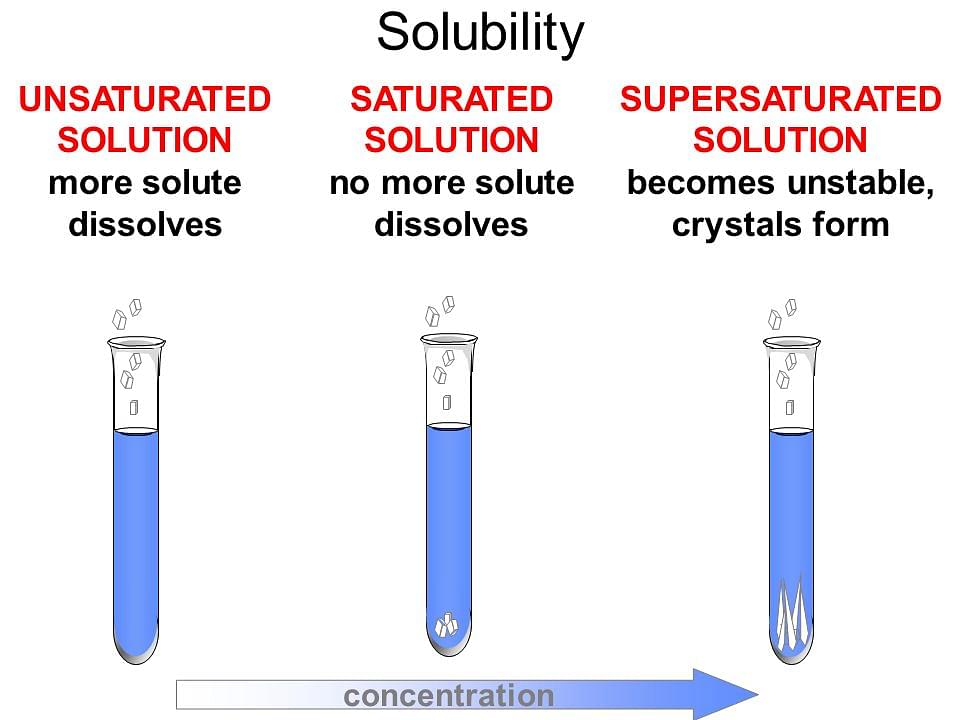
A: Yes, a supersaturated solution contains more solute than a saturated solution at a given temperature. However, these solutions are unstable and tend to crystallize quickly, returning to a saturated state.
Q: How can I determine if a solution is saturated?
A: You can determine if a solution is saturated by adding more solute. If the added solute dissolves, the solution is not saturated. If the added solute does not dissolve and remains at the bottom, the solution is saturated.
Q: What factors affect the solubility of a solute?
A: Several factors affect solubility, including:
- Temperature: Solubility generally increases with temperature.
- Pressure: Pressure affects the solubility of gases in liquids.
- Polarity: Solutes dissolve best in solvents with similar polarity. For example, polar solutes dissolve well in polar solvents like water, while non-polar solutes dissolve well in non-polar solvents like oil.
Tips for Creating Saturated Solutions
- Use precise measurements: Accurate measurements of both solute and solvent are essential for creating a saturated solution.
- Stir consistently: Stirring helps to ensure that the solute dissolves evenly and reaches equilibrium.
- Control temperature: Maintaining a constant temperature is crucial, as solubility changes with temperature.
- Allow for equilibration: Once the solution is saturated, allow it to reach equilibrium before making any further observations or measurements.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of saturated solutions is fundamental to various scientific and industrial applications. While it is not possible to create a saturated solution with sodium due to its reactivity with water, the principles of saturation apply to a wide range of solutes and solvents. By carefully controlling the variables involved, one can create saturated solutions and utilize their properties for a variety of purposes.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Concept of Saturated Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!