The Composition of the United States Congress: A Deep Dive into the Legislative Branch
Related Articles: The Composition of the United States Congress: A Deep Dive into the Legislative Branch
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Composition of the United States Congress: A Deep Dive into the Legislative Branch. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Composition of the United States Congress: A Deep Dive into the Legislative Branch

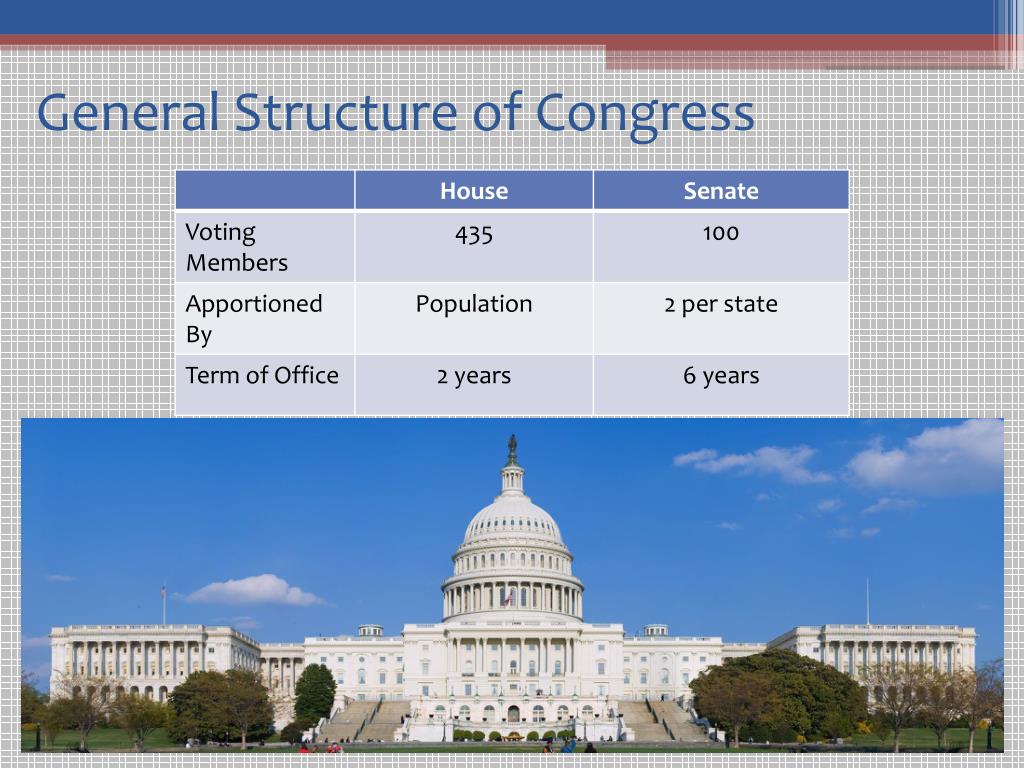
The United States Congress, the legislative branch of the federal government, is composed of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives. This bicameral structure, enshrined in the Constitution, represents a fundamental principle of American democracy, balancing the interests of states and the people. Understanding the makeup of Congress is essential for comprehending the dynamics of American politics and the legislative process.
The House of Representatives: The People’s Chamber
The House of Representatives is the lower chamber of Congress, with 435 members elected from congressional districts across the 50 states. The number of representatives each state receives is determined by its population, as established by the decennial census. This ensures representation based on population, making the House the chamber most directly accountable to the people.
The Senate: The States’ Chamber
The Senate, the upper chamber of Congress, consists of 100 members, two from each state, regardless of population. This structure gives equal representation to each state, regardless of size, ensuring that smaller states have a voice in national policy. Senators are elected by the entire state, providing a broader perspective than the district-based representation in the House.
The Legislative Process: A System of Checks and Balances
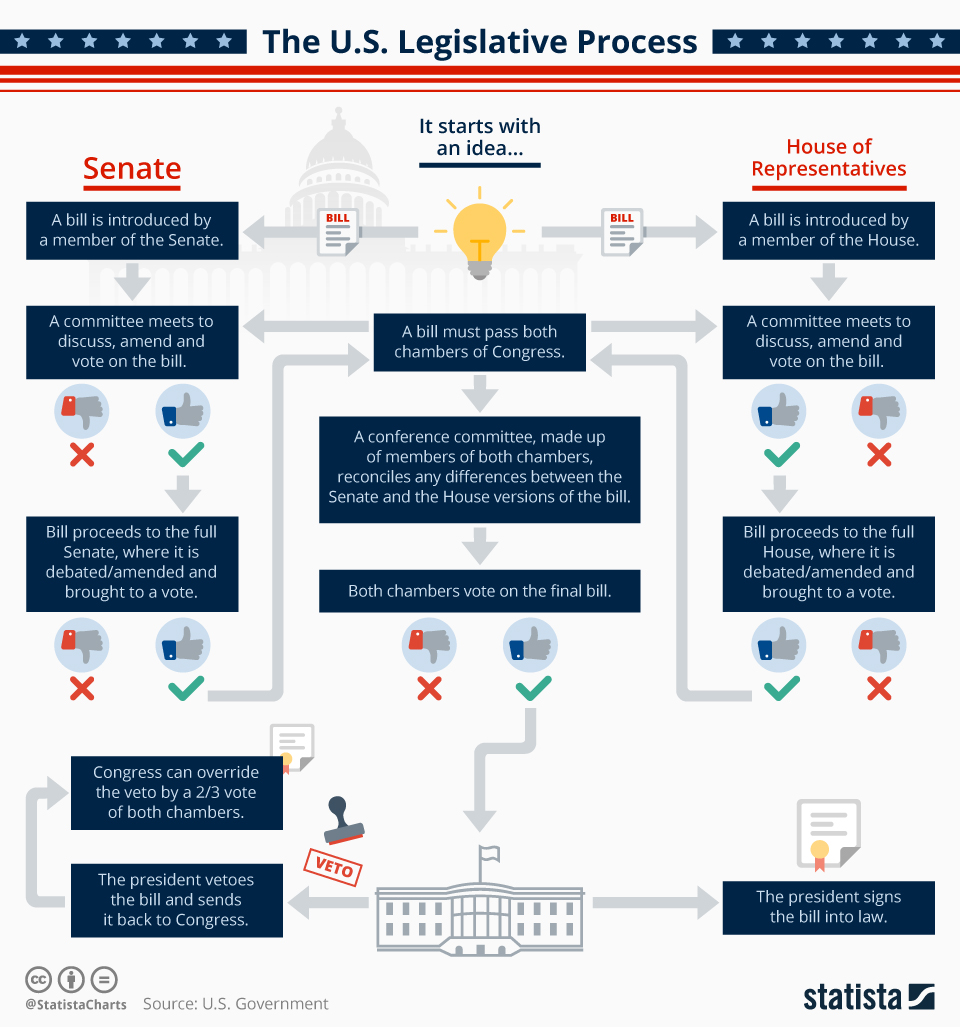
The bicameral structure of Congress serves as a crucial element in the system of checks and balances that defines the American political system. The House and Senate must agree on the exact wording of any legislation before it can be sent to the President for signature. This process requires compromise and negotiation, ensuring that laws reflect the will of both the people and the states.
The Role of Political Parties in Congressional Dynamics
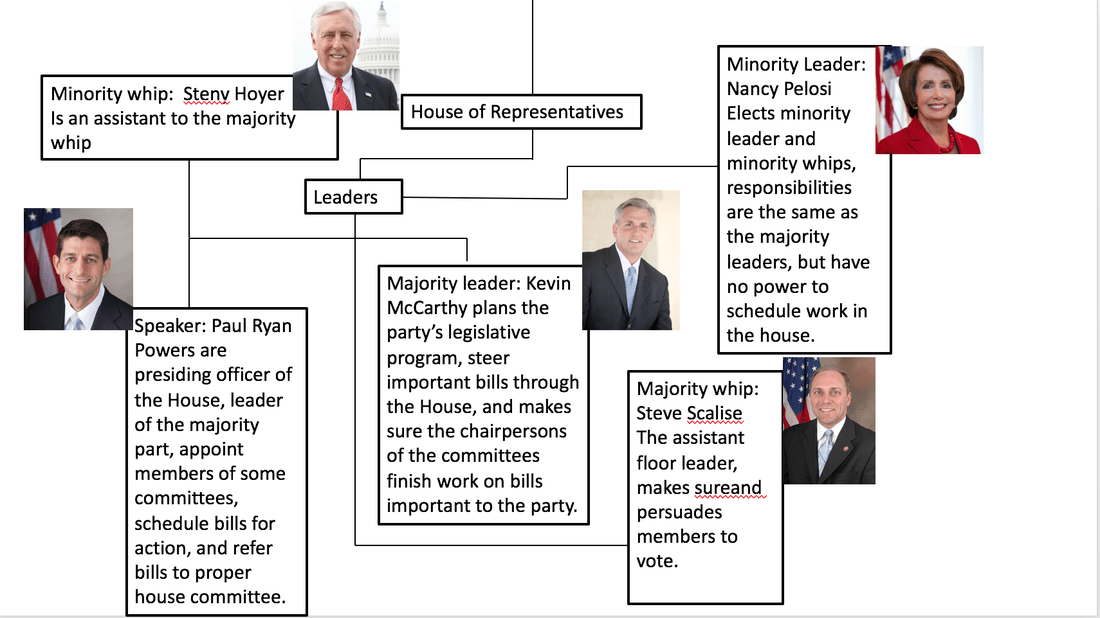
Political parties play a significant role in shaping the dynamics of Congress. The two major parties, the Democrats and Republicans, often hold a majority in one or both chambers. The majority party controls the leadership positions in each chamber, including the Speaker of the House and the President Pro Tempore of the Senate. These leaders influence the legislative agenda and the flow of bills through Congress.
The Power of Committees in the Legislative Process
Both the House and Senate are organized into specialized committees, each focusing on a specific policy area, such as agriculture, education, or foreign affairs. These committees play a crucial role in the legislative process, conducting hearings, reviewing bills, and drafting legislation. The committee system allows for a more thorough and informed consideration of complex issues.
The Importance of Congressional Oversight
Beyond lawmaking, Congress plays a vital role in overseeing the executive branch. This oversight function ensures that the government operates efficiently and ethically. Congressional committees hold hearings and investigations to scrutinize executive actions, spending, and policies. This oversight function is a key element of the system of checks and balances.
The Significance of Congressional Elections
Congressional elections are held every two years for all members of the House and for one-third of the Senate. These elections provide an opportunity for the electorate to express their preferences on policy issues and to hold their elected representatives accountable. The results of these elections can significantly impact the direction of the country.
FAQs
Q: How long are the terms of office for members of Congress?
A: Representatives in the House serve two-year terms, while senators serve six-year terms.
Q: What are the qualifications to be a member of Congress?
A: To be a Representative, one must be at least 25 years old, a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and a resident of the state and district they represent. To be a Senator, one must be at least 30 years old, a U.S. citizen for at least nine years, and a resident of the state they represent.
Q: How do bills become laws?
A: A bill must be introduced in either the House or the Senate. It then goes through a series of steps, including committee review, floor debate, and voting in both chambers. If both chambers pass the bill in identical form, it is sent to the President for signature. The President can sign the bill into law, veto it, or allow it to become law without signature after 10 days.
Q: What are the major differences between the House and the Senate?
A: The House is larger and more directly representative of the people, while the Senate is smaller and more representative of the states. The House has more rules and procedures, while the Senate is more deliberative.
Tips for Engaging with Congress
- Contact your Representatives and Senators: Reach out to your elected officials to express your views on issues important to you.
- Attend town hall meetings: These events provide an opportunity to engage directly with your representatives and ask questions.
- Follow Congressional news and debates: Stay informed about the legislative process and the issues being debated in Congress.
- Support organizations that advocate for policies you believe in: Many organizations work to influence legislation and promote specific policy agendas.
- Consider running for office: If you are passionate about public service, consider running for a seat in Congress.
Conclusion
The composition of the United States Congress, with its bicameral structure, is a testament to the principles of representative democracy and checks and balances enshrined in the Constitution. The interplay between the House and the Senate, the influence of political parties, and the role of committees all contribute to the complex and dynamic process of lawmaking in the United States. Understanding the makeup of Congress is essential for understanding the workings of the American political system and for engaging in the democratic process.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Composition of the United States Congress: A Deep Dive into the Legislative Branch. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!